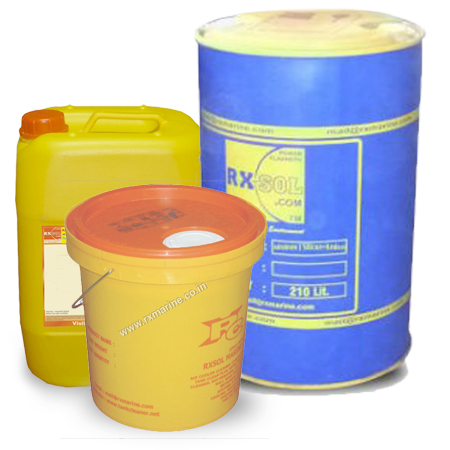
Description
If RXH is not acid enough to release a proton at alkaline pH, as it is the case with amines, then the reaction has to be carried out in two steps. During the first step the first EO mole is added at acid pH, so that the amine is transformed in ammonium. The reaction produce the mono-, di- and tri-ethanol amines.
Proton release from ammonium NH4+ → NH3 + H+ (here RX– is NH3) Then, the three condensation reactions:
NH3 + EO → NH2CH2CH2OH (mono-ethanol amine MEA)
NH2CH2CH2OH + EO → NH(CH2CH2OH)2 (di-ethanol amine DEA)
NH-(CH2CH2OH)2 + EO → N(CH2CH2OH)3 (tri-ethanol amine TEA)
With an alkyl amine, first the alkyl ammoniumion is formed and it is deprotonated:
RNH3+ → RNH2 + H+ (here RX– is RNH2)
RNH2 + EO → RNH-CH2CH2OH (mono-ethanol alkyl amine)
RNH-CH2CH2OH + EO → RN(CH2CH2OH)2 (di-ethanol alkyl amine)
Once the ethanol amine is attained, the EO polycondensation is carried out at alkaline pH as previously. In many instance the first ethoxylation is stopped when the monoethanol alkyl amine is formed in order to avoid the polycondensation in more than one chain.